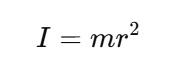What is Moment of Inertia and Why is it Important for Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 System of Particles and Rotational Motion?
Moment of Inertia (I) is the rotational equivalent of mass and it is used to measure an object's resistance to changes in its rotational motion. I is based on the mass of the object and how it is distributed relative to the axis of rotation. The formula to measure the moment of inertia is -
m stands
Similar Questions for you
|Δp| = 2mu sinθ = 2 × 5 × 10? ³ × 5√2 × (1/√2) = 5 × 10? ² kg m s? ¹
⇒ x = 5
An example of the periodic motion is Earth's revolution. In this, the motion repeats itself after regular intervals of time. In oscillatory motion, the object moves back and forth about a mean position like a vibrating spring or pendulum. It is a type of periodic motion. Although, oscillatory motion
When without slipping a body rotates and translates simultaneously is called rolling motion, such as a wheel on a road. It is the combination of rotatory and translatory motion. The point of contact has zero velocity relative to the surface in pure rolling. It is a condition in which there is no sli
According to the Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 System of Particles and Rotational Motion, for a rigid body to be in complete equilibrium, two conditions should be met:
- Net external torque = 0 (rotational equilibrium)
- Net external force = 0 (translational equilibrium)
The condition for equilibrium in rotat
To master the Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 Motion In A Plane, the students need to focus on thoroughly understanding vectors, and practice problems involving circular motion and projectile, for clarity, students should draw diagrams. They should memorize the key formulas, solve NCERT examples and atte
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering