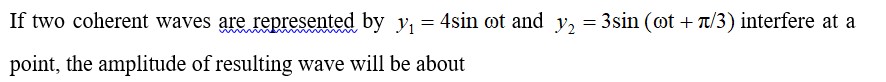8.27 For M2+/M and M3+/M2+ systems the E V values for some metals are as follows: Cr 2+/Cr - 0.9V Cr 3 /Cr 2+ -0.4 V Mn2+/Mn -1.2V Mn3+/Mn2+ +1.5 V Fe2+/Fe -0.4V Fe3+/Fe2+ +0.8 V Use this data to comment upon:
(i) The stability of Fe3+ in acid solution as compared to that of Cr3+ or Mn3+
(ii) The ease with which iron can be oxidised as compared to a similar process for either chromium or manganese metal.
8.27 For M2+/M and M3+/M2+ systems the E V values for some metals are as follows: Cr 2+/Cr - 0.9V Cr 3 /Cr 2+ -0.4 V Mn2+/Mn -1.2V Mn3+/Mn2+ +1.5 V Fe2+/Fe -0.4V Fe3+/Fe2+ +0.8 V Use this data to comment upon:
(i) The stability of Fe3+ in acid solution as compared to that of Cr3+ or Mn3+
(ii) The ease with which iron can be oxidised as compared to a similar process for either chromium or manganese metal.
8.27 (i) Reduction potential tells us the ease with which the Metal can get reduced, As E° for Cr3+/Cr2+ is negative (–0.4 V), this means that Cr3+ ions in solution cannot be reduced to Cr2+ ions i.e., Cr3+ ions are very stable. As a further comparison of E° values show that Mn3+ ions more readily t
Similar Questions for you
K2Cr2O7 + H2O2 + H2SO4->
Potassium permanganate in alkaline medium oxidise lodide to lodate.
Compound A is
KMnO4 decomposes upon heating at 513 K and forms K2MnO4 and MnO2.
2KMnO4
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering