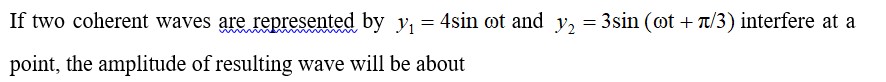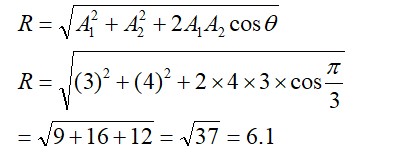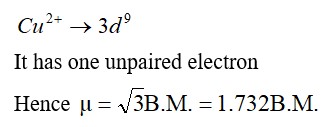8.30 Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to:
(i) Electronic configuration
(ii) Atomic and ionic sizes
(iii) Oxidation state
(iv) Chemical reactivity.
8.30 Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to:
(i) Electronic configuration
(ii) Atomic and ionic sizes
(iii) Oxidation state
(iv) Chemical reactivity.
8.30
| Lanthanoids | Actinoids |
Electronic Configuration | It is represented by [Xe]4fx5dy6s2, where x varies from 0 to 14 and y= 0 or 1 | It is represented by [Rn]5fx6dy7s2, where x varies from 0 to 14 and y= 0 or 1. |
Oxidation state | Generally shows +3 oxidation state only in some cases it is +2 or +4 but never greater than +4 | It has +3 oxidation state but also shows higher oxidation states such as +4, +5, +6, +7. |
Atomic and ionic sizes | Ionic radii of M3+ions decrease in size with increase in atomic number this is called as lanthanoid contraction. | There is a gradual decrease in the size of M3+ ions across the series, this is known as actinoid contraction. |
Chemical Reactivity | Lanthanoids are less reactive in nature and form oxides, sulphides, nitrides etc. They have a lesser tendency to form complexes. | They are highly reactive in nature when they are in the finely divided state. They have a higher tendency to form complexes and even react with non-metals at moderate temperature. |
Actinoid Contraction > Lanthanoid contraction
Lanthanoids show lanthanoid contraction due to which their size is quite small as compared to actinoids although there is actinoid contraction also lanthanoid contraction has more impact on elements as there is one shell less than actinoids, so lanth
Similar Questions for you
K2Cr2O7 + H2O2 + H2SO4->
Potassium permanganate in alkaline medium oxidise lodide to lodate.
Compound A is
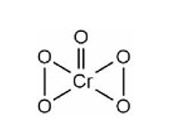
KMnO4 decomposes upon heating at 513 K and forms K2MnO4 and MnO2.
2KMnO4
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering