6. Find the values of x, y and z from the following equations:
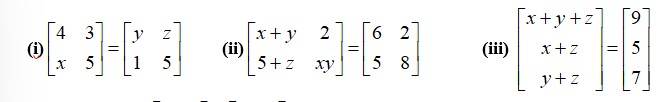
6. Find the values of x, y and z from the following equations:
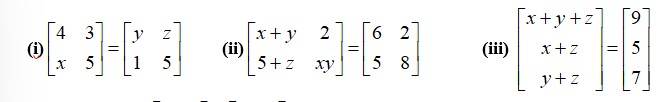
(i)
corresponding
By equating the elements of the matrices, we get,
x= 1
y= 4
z= 3.
(ii)
By equating the corresponding elements of the matrices we get,
x+ y = 6 (I)
5 + Z = 5
xy = 8
x
putting eq in (1) we get
+ y = 6.
8 + y2 = 6y
y2 6y + 8 = 0.
y2 - 4y - 2y + 8 = 0
y (y-4) -2 (y-4) = 0
(y-4) (y-2) = 0
y=
Similar Questions for you
Let
Given ...(1)
∴ x1 + z1 = 2 … (2)
x2 + z2 = 0 … (3)
x3 + z3 = 0 &nb
g (x) = px + q
Compare 8 = ap2 …………… (i)
-2 = a (2pq) + bp
0 = aq2 + bq + c
=>4x2 + 6x + 1 = apx2 + bpx + cp + q
=> Andhra Pradesh = 4 ……………. (ii)
6 = bp
1 = cp + q
From (i) & (ii), p = 2, q = -1
=> b = 3, c = 1, a = 2
f (x) = 2x2 + 3x + 1
f (2) = 8 + 6 + 1 = 15
g (x) = 2x – 1
g (2) = 3
Kindly consider the following figure
B = (I – adjA)5
Kindly consider the following figure
B = (I – adjA)5
System of equation is
R1 – 2 R2, R3 – R2
System of equation will have no solution for ![]() = -7.
= -7.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Maths Ncert Solutions class 12th 2026
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
