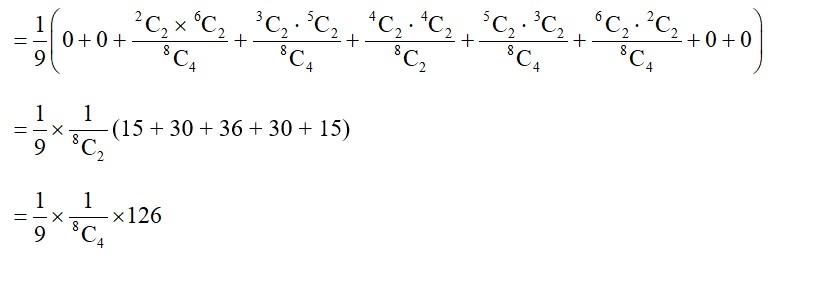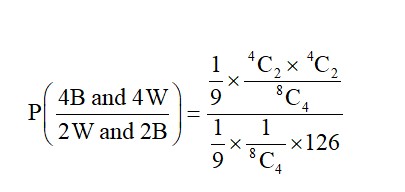Let in a Binomial distribution, consisting of 5 independent trials, probabilities of exactly 1 and 2 successes be 0.4096 and 0.2048 respectively. Then the probability of getting exactly 3 successes is equal to :
Let in a Binomial distribution, consisting of 5 independent trials, probabilities of exactly 1 and 2 successes be 0.4096 and 0.2048 respectively. Then the probability of getting exactly 3 successes is equal to :
This is a binomial probability problem with n=5. Let p be the probability of success and q be the probability of failure.
Given P (X=1) =? C? p¹q? = 5pq? = 0.4096 — (I)
Given P (X=2) =? C? p²q³ = 10p²q³ = 0.2048 — (II)
Divide (I) by (II): (5pq? ) / (10p²q³) = 0.4096 / 0.2048 = 2.
(1/2) * (q/p) = 2 ⇒ q/
Similar Questions for you
P (2 obtained on even numbered toss) = k (let)
P (2) =
P (
If x = 0, y = 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
If x = 1, y = 7, 8, 9, 10
If x = 2, y = 8, 9, 10
If x = 3, y = 9, 10
If x = 4, y = 10
If x = 5, y = no possible value
Total possible ways = (5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1) * 2
= 30
Required probability
P (2W and 2B) = P (2B, 6W) × P (2W and 2B)
+ P (3B, 5W) × P (2W and 2B)
+ P (4B, 4W) × P (2W and 2B)
+ P (5B, 3W) × P (2W and 2B)
+ P (6B, 2W) × P (2W and 2B)
(15 + 30 + 36 + 30 + 15)
Let probability of tail is
⇒ Probability of getting head =
∴ Probability of getting 2 heads and 1 tail
ax2 + bx + c = 0
D = b2 – 4ac
D = 0
b2 – 4ac = 0
b2 = 4ac
(i) AC = 1, b = 2 (1, 2, 1) is one way
(ii) AC = 4, b = 4
(iii) AC = 9, b = 6, a = 3, c = 3 is one way
1 + 3 + 1 = 5 way
Required probability =
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Maths Ncert Solutions class 12th 2026
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering