Let P(x) be a real polynomial of degree 3 which vanishes at x = -3. Let P(x) have local minima at x = 1, local maxima at x = -1 and ∫??¹ P(x)dx = 18, then the sum of all the coefficients of the polynomial P(x) is equal to......
Let P(x) be a real polynomial of degree 3 which vanishes at x = -3. Let P(x) have local minima at x = 1, local maxima at x = -1 and ∫??¹ P(x)dx = 18, then the sum of all the coefficients of the polynomial P(x) is equal to......
P' (x) = a (x-1) (x+1) = a (x²-1).
P (x) = ∫ P' (x) dx = a (x³/3 - x) + b.
Given P (-3) = 0 ⇒ a (-9+3) + b = 0 ⇒ b = 6a.
Given ∫ P (x)dx = 18. Assuming the integration is over a symmetric interval like [-c, c] and using the fact that a (x³/3-x) is an odd function, ∫ (a (x³/3 - x)dx = 0. Then ∫ b dx = 1
Similar Questions for you
option (C) is incorrect, there will be minima.
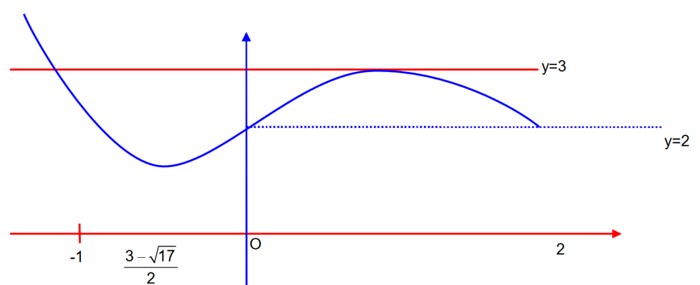
absolute minimum
absolute maximum = 3
If f(x) has maximum value at x = 1 then
……..(i)
……..(ii)
From (i) and (ii) we get
OP2 = x2 = y2
y = ex, y’ = ex,
slope of normal =
By hit and trial we get
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Maths Applications of Derivatives 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
