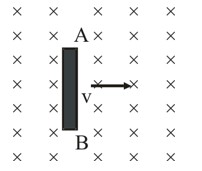
6.11 Suppose the loop in Exercise 6.4 is stationary but the current feeding the electromagnet that produces the magnetic field is gradually reduced so that the field decreases from its initial value of 0.3 T at the rate of 0.02 T s–1. If the cut is joined and the loop has a resistance of 1.6 Ω, how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat? What is the source of this power?
6.11 Suppose the loop in Exercise 6.4 is stationary but the current feeding the electromagnet that produces the magnetic field is gradually reduced so that the field decreases from its initial value of 0.3 T at the rate of 0.02 T s–1. If the cut is joined and the loop has a resistance of 1.6 Ω, how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat? What is the source of this power?
6.11 The area of the rectangular coil, A = 8 16 = 16
Initial value of the magnetic field, = 0.3 T
Rate of decrease of the magnetic field, = 0.02 T/s
From the relation of induced emf e = , where is the change in the flux linkage with the coil = A
Hence, e = = A = 16 = 3.2 V
Resistance in the
Similar Questions for you
Kindly go through the solution
Bv = B sin 60°
->
M = φ? /I? = (B? A? )/I? = [ (μ? I? /2R? )πR? ²]/I?
[Diagram of two concentric coils]
M = (μ? πR? ²)/ (2R? )
M ∝ R? ²/R?
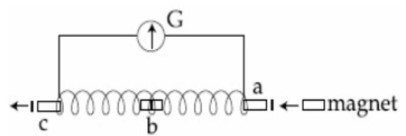
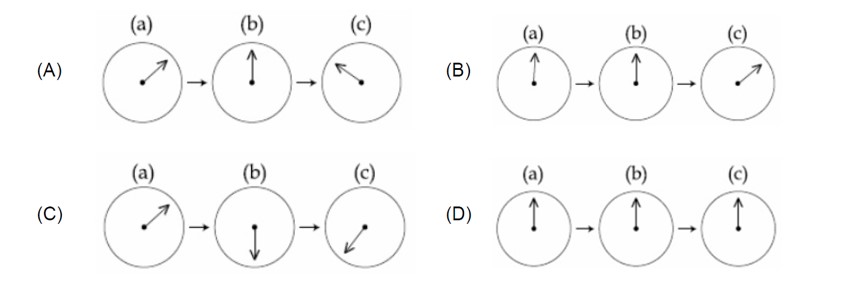
(A) The magnet's entry
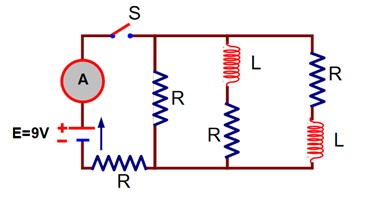
R =
L = 2 mH
E = 9V
Just after the switch ‘S’ is closed, the inductor acts as open circuit.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2026
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering