A ballon filled with helium rises against gravity increasing its potential energy. The speed of the ballon also increases as it rises. How do you reconcile this with the law of conservation of mechanical energy? You can neglect viscous drag of air and assume that density of air is constant.
A ballon filled with helium rises against gravity increasing its potential energy. The speed of the ballon also increases as it rises. How do you reconcile this with the law of conservation of mechanical energy? You can neglect viscous drag of air and assume that density of air is constant.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
V= volume of ballon
density of air
density of helium
V( )g= ma= mdv/dt= upthrust
Integrating with respect to t
V( )gt=mv
½ mv2= ½ m v2/m2 ( )2g2t2
= ½v2/m ( )2g2t2
= if the ballon rises to height h then s= ut +1/2at2
h=1/2at2= ½
so
Similar Questions for you
Using Newton’s formula,
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) conserving energy between “O” ans ”A”
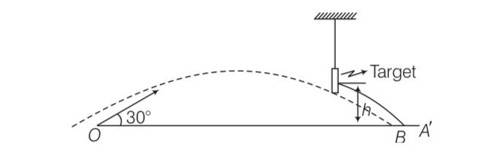
Ui + Ki = Uf + Kf
0+1/2mv2= mgh + 1/2mv’
(v’)2=v2-2gh = v’= ……….1
Let speed after emerging be v1 then
=1/2mv12=1/2[1/2mv’2]
1/2m(v1)2=1/4m(v’)2=1/4m[v2-2gh]
V1= ………….2
From eqn 1 and 2
So v1 = v’/
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b, d) When a man of mass m climbs up the staircases of height L, work done by the gravitational force on the man is mgl work done by internal muscular forces will be mgL as the change in kinetic is almost zero.
Hence total work done =-
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) m =150g =3/20kg
Time of contact =0.001s
U=126km/h=
V= -35m/s
Change in momentum of the ball = m (v-u)=
=21/2
F= dp/dt=- = - 1.05
Here – negative sign indicates that force will be opposite to the direction of movement of the ball be
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Six 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering