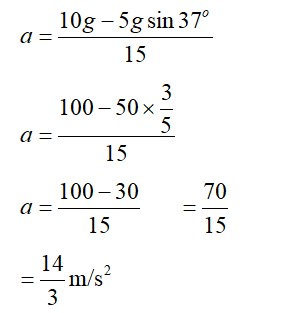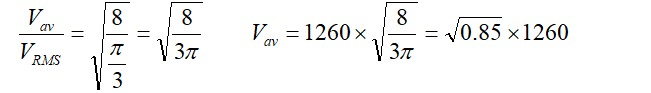A block of mass m = 1 kg slides with velocity v = 6 m/s on a frictionless horizontal surface and collides with a uniform vertical rod and sticks to it as shown. The rod is pivoted about O and swings as a result of the collision making angle θ before momentarily coming to rest. If the rod has mass M = 2 kg, and length l = 1 m, the value of θ is approximately: (take g = 10 m/s²)
A block of mass m = 1 kg slides with velocity v = 6 m/s on a frictionless horizontal surface and collides with a uniform vertical rod and sticks to it as shown. The rod is pivoted about O and swings as a result of the collision making angle θ before momentarily coming to rest. If the rod has mass M = 2 kg, and length l = 1 m, the value of θ is approximately: (take g = 10 m/s²)
By Conservation of Angular Momentum (COAM) about O, just before and after the collision:
Initial angular momentum L? = mv?
Final angular momentum L? = Iω? = (I_rod + I_block)ω? = (M? ²/3 + m? ²)ω?
L? = L?
mv? = (M? ²/3 + m? ²)ω?
ω? = mv / (M? /3 + m? ) = (16) / (21/3 + 1*1) = 6 / (5/3) = 18/5 rad/s
By
Similar Questions for you
= 0.92 * 1260 = 1161 m/s
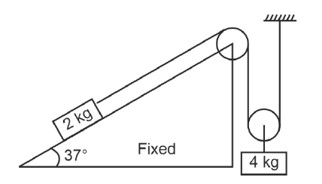
For 2 kg block
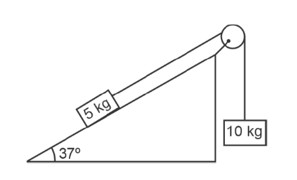
T – 2g sin37 = 2a . (i)
For 4 kg block
4g – 2T =
2g – T = a . (ii)
T = (2g – a)
2g – a – 2g × = 2a
3a = 2g ×
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering