A magnetic field B is confined to a region r ≤ a and points out of the paper (the z-axis), r = 0 being the centre of the circular region. A charged ring (charge = Q) of radius b, b> a and mass m lies in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The ring is free to rotate and is at rest. The magnetic field is brought to zero in time Δt. Find the angular velocity ω of the ring after the field vanishes.
A magnetic field B is confined to a region r ≤ a and points out of the paper (the z-axis), r = 0 being the centre of the circular region. A charged ring (charge = Q) of radius b, b> a and mass m lies in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The ring is free to rotate and is at rest. The magnetic field is brought to zero in time Δt. Find the angular velocity ω of the ring after the field vanishes.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Since, the magnetic field is brought to zero in time? t, the magnetic flux linked with the ring also reduces from maximum to zero. This, in turn, induces an emf in ring by the
phenomenon of EMI. The induces emf causes the electric fie
Similar Questions for you
Kindly go through the solution
Bv = B sin 60°
->
M = φ? /I? = (B? A? )/I? = [ (μ? I? /2R? )πR? ²]/I?
[Diagram of two concentric coils]
M = (μ? πR? ²)/ (2R? )
M ∝ R? ²/R?
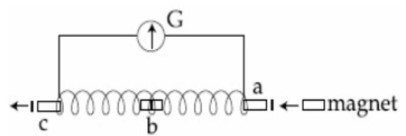
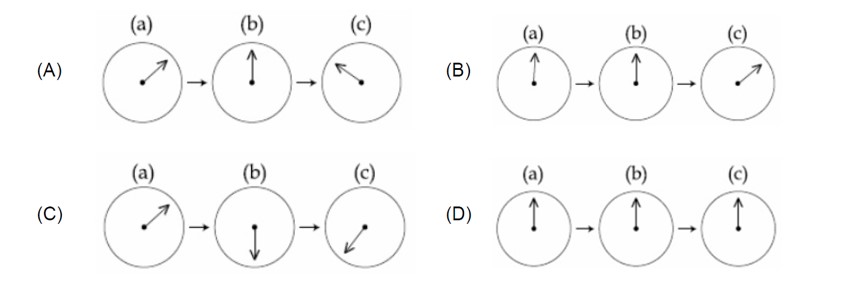
(A) The magnet's entry
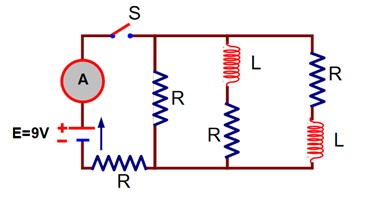
R =
L = 2 mH
E = 9V
Just after the switch ‘S’ is closed, the inductor acts as open circuit.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2026
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering