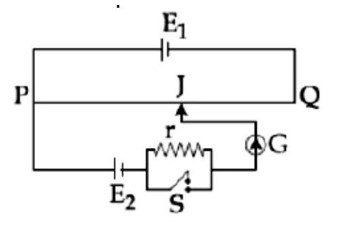
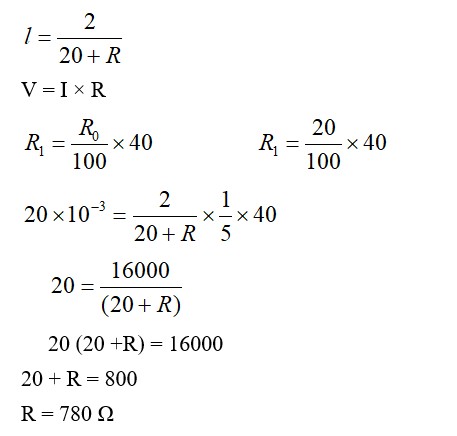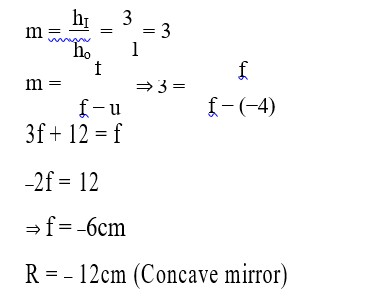A potentiometer wire PQ of 1 m length is connected to a standard cell E₁. Another cell E₂ of emf 1.02 V is connected with a resistance 'r' and switch S (as shown in figure). With switch S open, the null position is obtained at a distance of 49 cm from Q. The potential gradient in the potentiometer wire is:
A potentiometer wire PQ of 1 m length is connected to a standard cell E₁. Another cell E₂ of emf 1.02 V is connected with a resistance 'r' and switch S (as shown in figure). With switch S open, the null position is obtained at a distance of 49 cm from Q. The potential gradient in the potentiometer wire is:
Option 1 - <p>0.04 V/cm<br><!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><br><!--[endif]--></p>
Option 2 - <p>0.01 V/cm</p>
Option 3 - <p>0.02 V/cm<br><!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><br><!--[endif]--></p>
Option 4 - <p>0.03 V/cm</p>
4 Views|Posted 5 months ago
Asked by Shiksha User
1 Answer
A
Answered by
5 months ago
Correct Option - 3
Detailed Solution:
V_PQ * (49/100). 1.02 = V_PQ * 0.49. V_PQ ≈ 2.08V.
Potential gradient = 2.08V/100cm = 0.0208 V/cm.
Similar Questions for you
Ohm's law is valid if I depends on V' linearly.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
66K
Colleges
|
1.2K
Exams
|
6.9L
Reviews
|
1.8M
Answers
Learn more about...

Physics Current Electricity 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
or
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
or
See what others like you are asking & answering