A rod of length l and negligible mass is suspended at its two ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths (Fig. 9.4). The cross-sectional areas of wires A and B are 1.0 mm2 and 2.0 mm2, respectively. YAl=70 and Ysteel= 200
(a) Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have equal stresses in both the wires
(b) Mass m should be suspended close to B to have equal stresses in both the wires
(c) Mass m should be suspended at the middle of the wires to have equal stresses in both the wires
(d) Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have equal strain in both wires
A rod of length l and negligible mass is suspended at its two ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths (Fig. 9.4). The cross-sectional areas of wires A and B are 1.0 mm2 and 2.0 mm2, respectively. YAl=70 and Ysteel= 200
(a) Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have equal stresses in both the wires
(b) Mass m should be suspended close to B to have equal stresses in both the wires
(c) Mass m should be suspended at the middle of the wires to have equal stresses in both the wires
(d) Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have equal strain in both wires
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (d) Let mass m is placed at x from the end B respectively.
TA and TB be the tensions in wire A and wire B respectively.
For the rotational equilibrium of the system,
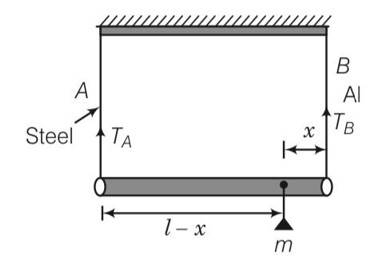
TBx-TA(l-x)=0
=
Stress in wire A = SA=
Stress in wire B = SB=
Similar Questions for you
If is Poisson’s ratio,
Y = 3K (1 - 2 ) ……… (1)
and Y = 2 ……… (2)
With the help of equations (1) and (2), we can write
dm = (m/L)dx
∴ T = (mω²/2L) (L² - x²)
∴ ΔL = ∫? (mω²/2Lπr²Y) (L² - x²)dx
= ΔL = mω²L²/3πr²Y
Initially S? L = 2m
S? L = √2² + (3/2)²
S? L = 5/2 = 2.5 m
? x = S? L - S? L = 0.5 m
So since λ = 1 m. ∴? x = λ/2
So white listener moves away from S? Then? x (= S? L − S? L) increases and hence, at? x = λ first maxima will appear.? x = λ = S? L − S? L.
1 = d - 2 ⇒ d = 3 m.
Loss in elastic potential energy = Gain in KE
½ (YA/L)x² = ½mv²
0.5 × (0.5×10? × 10? / 0.1) × (0.04)² = 20×10? ³ v²
0.5 × (5×10²) × 1.6×10? ³ = 20×10? ³ v²
0.4 = 20×10? ³ v²
v² = 20 => v = √20 ≈ 4.47 m/s
(Re-checking calculations)
0.5 * ( (0.5e9 * 1e-6) / 0.1) * (0.04)^2 = 0.5 * (5e2) * 1.6e-3 = 4.
0.5 * 2
As we know that
If length and diameter both are doubled
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Nine 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
