In nature, the failure of structural members usually result from large torque because of twisting or bending rather than due to tensile or compressive strains. This process of structural breakdown is called buckling and in cases of tall cylindrical structures like trees, the torque is caused by its own weight bending the structure. Thus the vertical through the centre of gravity does not fall within the base. The elastic torque caused because of this bending about the central axis of the tree is given by . Y is the Young's modulus, r is the radius of the trunk and R is the radius of curvature of the bent surface along the height of the tree containing the centre of gravity (the neutral surface). Estimate the critical height of a tree for a given radius of the trunk.
In nature, the failure of structural members usually result from large torque because of twisting or bending rather than due to tensile or compressive strains. This process of structural breakdown is called buckling and in cases of tall cylindrical structures like trees, the torque is caused by its own weight bending the structure. Thus the vertical through the centre of gravity does not fall within the base. The elastic torque caused because of this bending about the central axis of the tree is given by . Y is the Young's modulus, r is the radius of the trunk and R is the radius of curvature of the bent surface along the height of the tree containing the centre of gravity (the neutral surface). Estimate the critical height of a tree for a given radius of the trunk.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Consider the diagram according, the bending torque on the trunk of radius r of the tree =
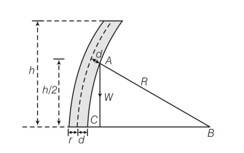
When the tree is about to buckle Wd=
If R>>h, then the centre of gravity is at a height l
From 2+ (h/2)2
If d <2+
So d = h2/8R
If wo is the weight /
Similar Questions for you
If is Poisson’s ratio,
Y = 3K (1 - 2 ) ……… (1)
and Y = 2 ……… (2)
With the help of equations (1) and (2), we can write
dm = (m/L)dx
∴ T = (mω²/2L) (L² - x²)
∴ ΔL = ∫? (mω²/2Lπr²Y) (L² - x²)dx
= ΔL = mω²L²/3πr²Y
Initially S? L = 2m
S? L = √2² + (3/2)²
S? L = 5/2 = 2.5 m
? x = S? L - S? L = 0.5 m
So since λ = 1 m. ∴? x = λ/2
So white listener moves away from S? Then? x (= S? L − S? L) increases and hence, at? x = λ first maxima will appear.? x = λ = S? L − S? L.
1 = d - 2 ⇒ d = 3 m.
Loss in elastic potential energy = Gain in KE
½ (YA/L)x² = ½mv²
0.5 × (0.5×10? × 10? / 0.1) × (0.04)² = 20×10? ³ v²
0.5 × (5×10²) × 1.6×10? ³ = 20×10? ³ v²
0.4 = 20×10? ³ v²
v² = 20 => v = √20 ≈ 4.47 m/s
(Re-checking calculations)
0.5 * ( (0.5e9 * 1e-6) / 0.1) * (0.04)^2 = 0.5 * (5e2) * 1.6e-3 = 4.
0.5 * 2
As we know that
If length and diameter both are doubled
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Nine 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
