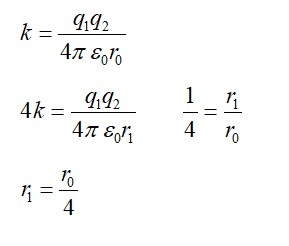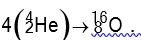The gravitational force between a H atom and a another particle of mass m will be given newton's law
F=GMm/r2 where r in km
(a) M=mproton+melectron
(b) M=mproton+melectron-
(c) M is not relate to the mass of the hydrogen atom
(d) M=mproton+melectron-(|V|)= magnitude of the potential energy of electron in H atom.
The gravitational force between a H atom and a another particle of mass m will be given newton's law
F=GMm/r2 where r in km
(a) M=mproton+melectron
(b) M=mproton+melectron-
(c) M is not relate to the mass of the hydrogen atom
(d) M=mproton+melectron-(|V|)= magnitude of the potential energy of electron in H atom.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation- F=GMm/r2
M=effective mass of hydrogen atom=mass of electron +mass of proton -B2/c
B.E of hydrogen atom = 13.6eV
Similar Questions for you
Q = [4 *4.0026 – 15.9994] *931.5 MeV
Q = 10.2 MeV
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering