The value of lim(n→∞) ([r] + [2r] + ... + [nr]) / n², where r is a non-zero real number and [r] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to r, is equal to:
The value of lim(n→∞) ([r] + [2r] + ... + [nr]) / n², where r is a non-zero real number and [r] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to r, is equal to:
Limit (n→∞) [[r] + [2r] + ... + [nr]] / n²
We know that x - 1 < [x] ≤ x.
Summing from k=1 to n for [kr]:
Σ(kr - 1) < Σ[kr] ≤ Σ(kr)
rΣk - Σ1 < Σ[kr] ≤ rΣk
r(n(n+1)/2) - n < Σ[kr] ≤ r(n(n+1)/2)
Divide by n²:
(r/2)(1 + 1/n) - 1/n < (Σ[kr])/n² ≤ (r/2)(1 + 1/n)
As n → ∞, both the left and right sides approach r/2.
By the Squeeze Theorem, the limit is r/2.
Similar Questions for you
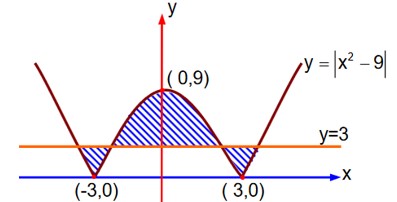
Required area = A
Note : No option in the question paper is correct.
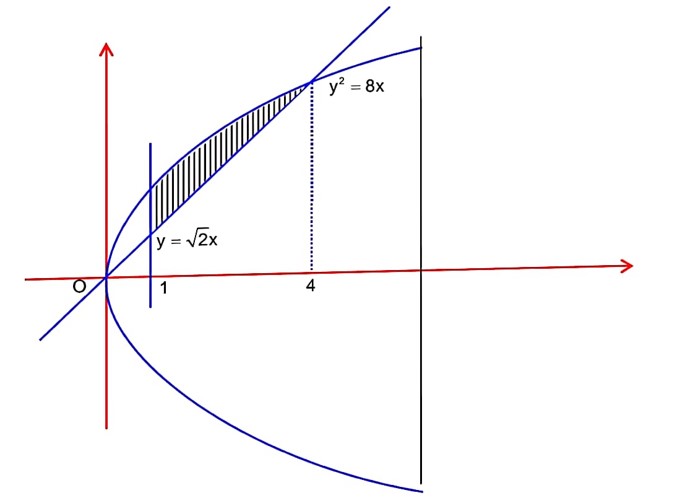
Required area = dx
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Maths Application of Integrals 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering