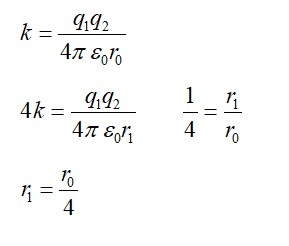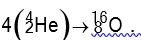13.8 The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive present with the stable carbon isotope . When the organism is dead, its interaction with the atmosphere (which maintains the above equilibrium activity) ceases and its activity begins to drop. From the known half-life (5730 years) of , and the measured activity, the age of the specimen can be approximately estimated. This is the principle of dating used in archaeology. Suppose a specimen from Mohenjo-Daro gives an activity of 9 decays per minute per gram of carbon. Estimate the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilization.
13.8 The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive present with the stable carbon isotope . When the organism is dead, its interaction with the atmosphere (which maintains the above equilibrium activity) ceases and its activity begins to drop. From the known half-life (5730 years) of , and the measured activity, the age of the specimen can be approximately estimated. This is the principle of dating used in archaeology. Suppose a specimen from Mohenjo-Daro gives an activity of 9 decays per minute per gram of carbon. Estimate the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilization.
13.8 Decay rate of living carbon-containing matter, R = 15 decay / min
Half life of , = 5730 years
Decay rate of the specimen obtained from the Mohenjo-Daro site, R' = 9 decays/min
Let N be the number of radioactive atoms present in a normal carbon-containing matter.
Let N' be the number of radioactiv
Similar Questions for you
Q = [4 *4.0026 – 15.9994] *931.5 MeV
Q = 10.2 MeV
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering